 transformer guide designed to convert 240V AC to 12V output” class=”wp-image-1623″/>
transformer guide designed to convert 240V AC to 12V output” class=”wp-image-1623″/>Transformers are the silent workhorses of our electrical infrastructure, managing voltage levels across everything from industrial grids to domestic appliances. One of the most common and critical applications of a transformer is to convert 240V AC mains electricity into a much safer and more usable 12V AC or DC supply. This voltage level is essential for operating low-power electronics, LED lighting, security systems, and various consumer devices.
But which type of transformer is suitable for this voltage reduction, and what factors should influence the selection?
This guide provides an in-depth overview of transformer types used for stepping down 240V AC to 12V, exploring technical parameters, real-world applications, market trends, and buyer insights—all optimized for technical accuracy and SEO relevance.
A step-down transformer reduces high input voltage to a lower output voltage while maintaining the same frequency. In the case of reducing 240V to 12V, the transformer’s turns ratio is the defining parameter. A primary coil with 20 times the turns of the secondary coil will produce the desired 12V output from a 240V input.
Types of step-down transformers include:
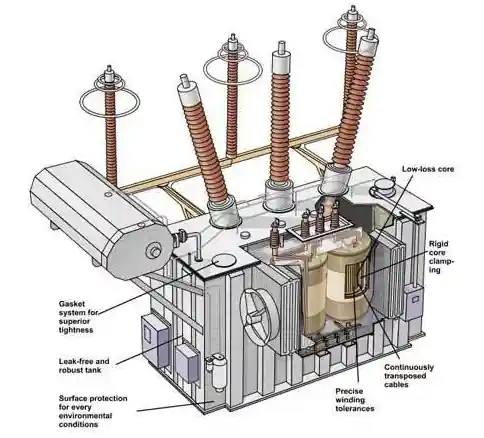
A 12V supply is safe, energy-efficient, and compatible with a wide range of low-voltage systems. Key application areas include:
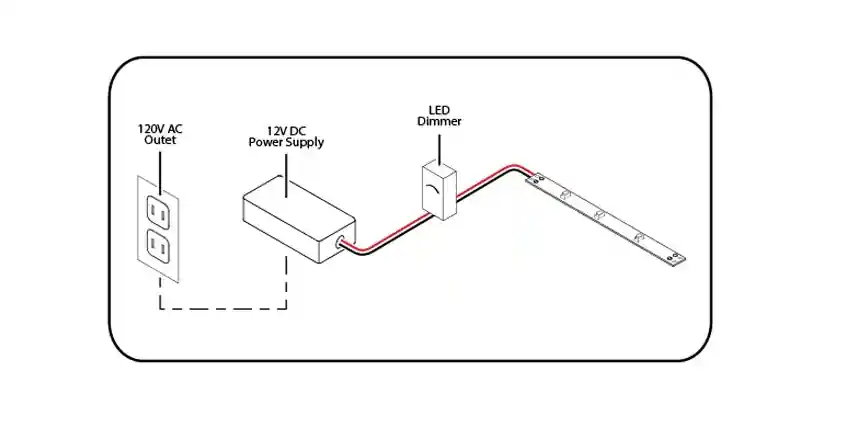
Globally, the demand for 12V applications is growing due to the proliferation of smart home devices, energy-efficient lighting, and mobile electronics. According to industry surveys and publications from IEEE and IEEMA, there is increasing preference for modular, compact, and high-efficiency transformers in both residential and commercial markets.
In particular, LED lighting retrofits in older buildings drive demand for AC-to-DC 12V transformers, as they ensure compatibility with standard 240V supply without requiring a complete rewiring of systems.
Here’s a detailed look at the most suitable transformer types:
Pros:
Cons:
Pros:
Cons:
Pros:
Cons:
Pros:
Cons:
When choosing a transformer to convert 240V to 12V, pay attention to the following specifications:
| Parametri | Relevance |
|---|---|
| Tulojännite | Rated for 230V–250V AC (nominal 240V) |
| Lähtöjännite | 12V AC or DC, depending on application |
| Taajuus | 50 Hz or 60 Hz, depending on region |
| Power Rating (VA) | Match with total load power plus 20–30% safety margin |
| Mounting Type | Chassis, panel, DIN rail, or PCB |
| Eristysluokka | Higher class (e.g., Class B or F) for thermal reliability |
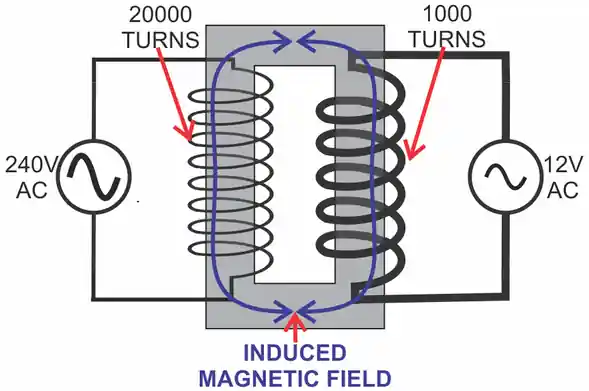
While transformers and adapters may seem similar, they serve distinct purposes:
Example:
If your application needs 12V AC (e.g., halogen lights), use a simple transformer.
If your device requires 12V DC (e.g., routers, cameras), you’ll need a transformer + rectifier or a ready-made AC-DC adapter.
No. A 12V transformer outputs AC by default. To use it for DC devices, you need a rectifier circuit (diode bridge + filter capacitor or regulator).
It may overheat, become damaged, or cause voltage solutions drops under load. Always size the transformer 20–30% higher than your actual load.
Yes—for applications that require compactness, low noise, and high efficiency. However, laminated transformers are more affordable and easier to source for basic setups.
To reduce a 240V AC supply to 12V, the most suitable transformer depends on the output type (AC or DC), application, and load requirements. For basic low-voltage lighting or appliances, a laminated core step-down transformer will suffice. For compact, high-efficiency designs—such as in audio equipment or sensitive electronics—a toroidal transformer may be preferred. And in modern digital electronics, switch-mode transformers deliver excellent performance where DC output is required.
Making the right transformer selection ensures not only operational safety and energy efficiency but also compliance with global standards. Whether you’re building a solar lighting circuit, installing a CCTV system, or designing embedded electronics, investing in the correct step-down transformer is key to long-term reliability.
Osoite: 555 Station Road, Liu Shi Town, Yueqing City, Wenzhou City, Zhejiangin maakunta, Kiina
Puh / WhatsApp:+86 180-5886-8393
Sähköposti: [email protected]
©2015 - PINEELE Kaikki oikeudet pidätetään.
Tämän asiakirjan sisältämän materiaalin jäljentäminen missä tahansa muodossa tai mediassa ilman PINEELE Electric Group Co., Ltd:n nimenomaista kirjallista lupaa on kielletty.
Jätä viestisi tänne! Lähetämme yksityiskohtaiset tekniset tiedot ja tarjouksen sinulle!