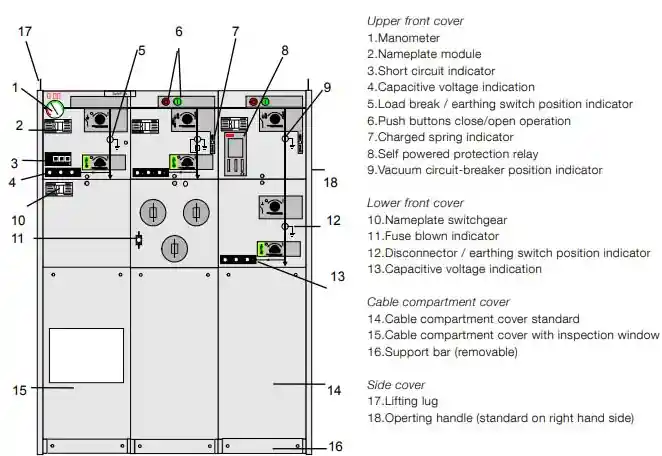
 Ring Main Unit guide showing circuit breaker, isolators, and switchgear compartments.” class=”wp-image-1598″/>
Ring Main Unit guide showing circuit breaker, isolators, and switchgear compartments.” class=”wp-image-1598″/>Ring Main Units (RMUs) are a vital component of medium-voltage power distribution networks, ensuring reliability, safety, and continuity of electrical supply. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the core working principle of RMUs, their applications, advantages, and technical nuances that set them apart in modern energy systems.
What is a Ring Main Unit (RMU)?
A Ring Main Unit is a compact, enclosed switchgear unit used in medium-voltage power distribution networks. It is typically installed in secondary distribution systems to manage and isolate electrical faults while ensuring continuous power flow to critical circuits.
Caratteristiche principali:
- Medium voltage rating (typically 11kV to 33kV)
- Enclosed in metal for safety and durability
- Includes load break switches, circuit breakers, and fuses
Working Principle of a Ring Main Unit
At the heart of the RMU is a “ring” configuration of conductors, allowing electricity to flow in multiple paths. This redundancy ensures that if one side of the loop fails or needs maintenance, the other side continues supplying power.
Typical Components Include:
- Load Break Switches (LBS): Interrupt normal load current
- Vacuum Circuit Breakers (VCB): Protect circuits from fault currents
- Earthing Switches: Ensure safety during maintenance
- Busbars and Isolators: Facilitate routing and disconnection
Working Steps:
- Power flows through either side of the ring.
- The LBS allows safe switching under load conditions.
- If a fault is detected, the VCB isolates the affected section.
- Maintenance crews can then safely work on the de-energized section without interrupting service elsewhere.
Application Fields
Ring Main Units are widely used across industries due to their safety, compactness, and efficiency.
- Urban power distribution grids
- Industrial zones and manufacturing plants
- Renewable energy integration (wind/solar farms)
- Hospitals, data centers, and airports

Market Trends and Industry Context
According to a report by IEEE and IEEMA, the demand for RMUs is surging due to urbanization, grid modernization, and renewable integration. Compact switchgear solutions are becoming essential for smart grid architecture and underground power distribution.
Notable Manufacturers:
- ABB: Offers SF6-insulated and eco-efficient RMUs
- Schneider Electric: Known for their SM6 and Ringmaster series
- Siemens: Delivers RMUs with digital monitoring capabilities
Technical Specifications (Typical Values)
| Parametro | Value |
|---|---|
| Tensione nominale | 11kV / 22kV / 33kV |
| Corrente nominale | Up to 630A |
| Short Circuit Rating | Up to 21kA |
| Insulation Type | SF6 or solid insulated |
| Operating Mechanism | Manual / Motorized |
| Protection | Overcurrent, Earth fault |
| Tipo di installazione | Interno/esterno |
How RMUs Differ from Other Switchgear
While RMUs fall under the broader switchgear category, their compact size, ring-based topology, e fault-tolerant architecture distinguish them.
| Feature | RMU | Conventional Switchgear |
| Design | Compact, sealed units | Larger, modular |
| Redundancy | Ring topology | Radial / single path |
| Maintenance | Minimal, sealed for life | Regular inspections required |
| Application | Distribution networks | Primary substations |
Selection & Purchasing Tips
When selecting an RMU, consider:
- Voltage & current ratings to match your network
- Type of insulation (SF6 vs. solid)
- Automation support for remote control and SCADA integration
- Manufacturer reputation and service network
Always consult with a certified electrical engineer or your local utility provider.
FAQs
A: Yes, when handled correctly. SF6 is non-toxic and inert but should be managed to avoid leaks. Many manufacturers now offer eco-friendly alternatives.
A: Absolutely. Their compact size and sealed design make them ideal for underground substations and densely populated areas.
A: Yes, especially for solar and wind power systems needing reliable grid connection and protection.
Understanding the working principle of Ring Main Units is crucial for professionals involved in power system planning and operation. Their unique configuration, reliability, and adaptability make RMUs a cornerstone of modern electrical infrastructure.
For deeper insights, consult resources from IEEE, Wikipedia, and official product documentation from ABB, Schneider, or Siemens.