Introduction
A 400kv substation guide is a critical part of the high-voltage power transmission network, ensuring the efficient transfer of electricity from power generation plants to distribution networks. These substations help manage power flow, protect electrical equipment, and support the integration of renewable energy sources.
This article explores the components, functions, types, applications, and future trends of 400kV substations.
What is a 400kV Substation?
A 400kV substation is designed to step up or step down electrical voltage levels, monitor transmission performance, and ensure the safety of power systems.
Why 400kV?
- Efficient long-distance power transmission with minimal energy loss.
- Ensures grid stability by managing large-scale power distribution.
- Supports industrial and urban power demand with high-capacity networks.
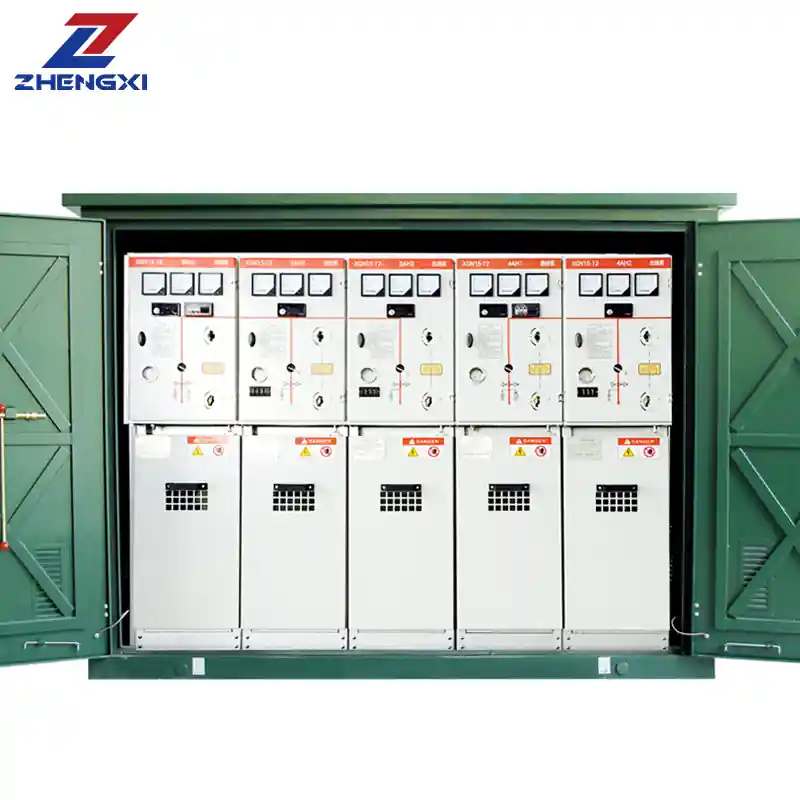

Key Components of a 400kV Substation
Each substation consists of various high-voltage equipment and control systems.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Power Transformer | Steps up/down voltage for transmission or distribution. |
| Circuit Breaker | Protects the grid by interrupting fault currents. |
| Busbars | Conduct electricity within the substation. |
| Disconnectors | Isolate equipment during maintenance. |
| Capacitor Banks | Improve power factor and voltage stability. |
| Surge Arresters | Protect against lightning and voltage surges. |
| SCADA System | Enables remote monitoring and control of the substation. |

Types of 400kV Substations
Based on insulation type and location, 400kV substations are classified as:
Air-Insulated Substation (AIS)
✔ Uses open-air insulation for electrical equipment.
✔ Cost-effective but requires more space.
✔ Commonly used in rural and suburban areas.
Gas-Insulated Substation (GIS)
✔ Compact design with SF6 gas insulation.
✔ Suitable for urban areas with limited space.
✔ Higher installation cost but lower maintenance.
Hybrid Substations
✔ Combination of AIS and GIS technologies.
✔ Balances cost and space efficiency.

Applications of 400kV Substations
400kV substations are widely used across different industries and locations.
| Application | Description |
|---|---|
| Power Plants | Connects electricity from generation stations to the grid. |
| Industrial Zones | Supplies high-voltage power to steel plants, oil refineries, and factories. |
| Urban Electricity Supply | Ensures reliable power for cities and commercial areas. |
| Railway Electrification | Provides power to high-speed trains and metro systems. |
| Renewable Energy Integration | Supports wind farms and solar plants for clean energy transmission. |

Importance of 400kV Substations
400kV substations are essential for modern energy infrastructure:
Enhancing Grid Stability
- Prevents power outages and fluctuations.
Supporting Renewable Energy
- Integrates solar and wind farms into the grid.
Minimizing Energy Losses
- Higher voltage reduces resistance losses over long distances.
Powering Industrial and Commercial Zones
- Essential for factories, data centers, and urban areas.

Key Considerations in 400kV Substation Design
When planning a 400kV substation, engineers focus on:
✔ Safety & Protection Systems – Fire suppression, fault detection, and grounding.
✔ Grid Compatibility – Meets national transmission regulations.
✔ Environmental Factors – Noise control and eco-friendly insulation.
✔ Future Expansion – Modular design for scalability.
Future Trends in 400kV Substations
Smart Grid Integration
- AI-powered automation for real-time monitoring.
♻ Eco-Friendly Insulation
- SF6-free GIS technology to reduce environmental impact.
Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS)
- Improves grid reliability and backup power.
