- 1. Radial Distribution System
- Overview:
- Key Features:
- Applications:
- Limitations:
- 2. Ring Main Distribution System
- Overview:
- Key Features:
- Applications:
- Technical Reference:
- 3. Loop Distribution System
- Overview:
- Key Features:
- Applications:
- Consideration:
- 4. Interconnected Distribution System
- Overview:
- Key Features:
- Applications:
- Standard Compliance:
- Market Trends and Adoption
- Comparison Table
- Selection Guide
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Power distribution systems are the backbone of modern electrical infrastructure, ensuring that electricity generated at power plants reaches homes, businesses, and industries efficiently and safely. Understanding the different types of power distribution systems is crucial for electrical engineers, contractors, and facility managers when planning or maintaining electrical networks. This article provides a comprehensive breakdown of the four primary types of power distribution systems.
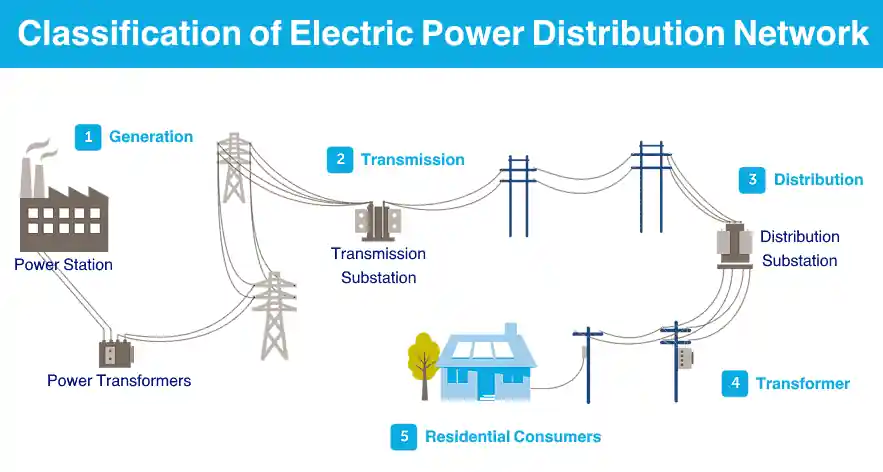
1. Radial Distribution System
Overview:
The radial system is the simplest and most commonly used configuration in residential and rural areas. Power flows in a single direction from the substation to the end users.
Key Features:
- One-way power flow
- Simple design and low cost
- Easy fault detection
Applications:
- Residential zones
- Rural electrification
Limitations:
- No backup path for power
- Entire branch loses power during a fault

2. Ring Main Distribution System
Overview:
A ring main system forms a closed loop where the power can flow in either direction, providing redundancy and improved reliability.
Key Features:
- Power can be rerouted
- Better load management
- Fault isolation without full outage
Applications:
- Urban residential complexes
- Industrial parks
Technical Reference:
- IEC 61936 and IEEE 141 standards recommend ring main units (RMUs) for medium-voltage applications.

3. Loop Distribution System
Overview:
The loop system is similar to the ring main but is open-ended, typically used in commercial and urban areas. It allows for selective switching between multiple sources.
Key Features:
- Partial redundancy
- Good for system maintenance without full shutdown
- Moderate cost and complexity
Applications:
- Commercial buildings
- Campus environments
- Mixed-use developments
Consideration:
- Requires well-designed switchgear for fault handling

4. Interconnected Distribution System
Overview:
The interconnected system is the most advanced and reliable setup. Multiple substations are connected through multiple feeders, allowing seamless power flow and redundancy.
Key Features:
- Highest reliability and flexibility
- Ideal for critical infrastructure
- Complex design and higher cost
Applications:
- Large industrial zones
- Metropolitan grids
- Hospitals and data centers
Standard Compliance:
- IEEE Std 1547, IEEE 80, IEC 60076
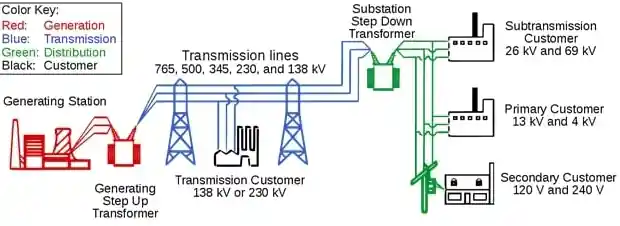
Market Trends and Adoption
According to IEEMA, the adoption of interconnected and loop systems is rising in urban smart grid development. ABB and Schneider Electric offer modular and automated solutions for ring and loop systems, optimizing performance through SCADA integration.
The push toward grid modernization and renewable energy integration also favors more adaptive systems like loop and interconnected models. The IEEE Smart Grid Report highlights how distribution automation (DA) technologies are key to future-ready networks.
Comparison Table
| Distribution Type | Cost | Reliability | Complexity | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Radial | Low | Low | Simple | Rural & basic residential areas |
| Ring Main | Moderate | Medium | Medium | Urban & medium-load industries |
| Loop | Moderate | Medium-High | Medium | Commercial & mixed developments |
| Interconnected | High | High | High | Critical & urban power networks |
Selection Guide
- Choose Radial for small-scale or rural applications with limited budget.
- Use Ring Main when uptime and maintainability are important.
- Opt for Loop in commercial setups that need operational flexibility.
- Go with Interconnected systems for mission-critical or city-wide reliability.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
The interconnected distribution system offers the highest reliability due to its multiple power sources and redundancy paths.
Yes, especially in urban apartment complexes where medium-voltage reliability is essential.
Yes, but it involves adding switchgear guide and reconfiguring feeder paths, often used during urban infrastructure upgrades.
Understanding the four types of power distribution systems—Radial, Ring Main, Loop, and Interconnected—is vital for modern power network planning. While each type has its strengths and suitable applications, choosing the right one depends on factors such as cost, criticality, scalability, and urban density.
Get a printable version of this page as a PDF.