- Core Concepts Explained
- What Is a Compact Substation?
- What Is a Conventional Substation?
- Application Areas
- Compact Substation Applications:
- Conventional Substation Applications:
- Technical Parameters & Structural Differences
- Market Trend and Industry Adoption
- Selection Criteria: Which One to Choose?
- Choose a Compact Substation when:
- Choose a Conventional Substation when:
- Benefits Summary
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
As the global demand for power grows, the need for efficient, space-saving, and modular substation solutions becomes increasingly important. This has led to the rising popularity of compact substations, also known as packaged substations or prefabricated substations. But how do they compare with traditional conventional substations? This article offers a detailed comparison between compact and conventional substations, helping engineers, developers, and utilities make informed infrastructure decisions.
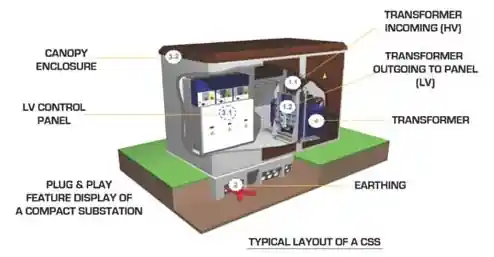
Core Concepts Explained
What Is a Compact Substation?
A compact substation is a preassembled, factory-tested power distribution unit that integrates the transformer, medium-voltage switchgear, and low-voltage distribution board into a single enclosure. It is fully enclosed, often weatherproof, and designed for plug-and-play installation.
What Is a Conventional Substation?
A conventional substation is a custom-built power distribution facility with separated components (e.g., switchgear room, transformer yard, control room) installed on-site. It requires civil construction and is typically larger in footprint.
Application Areas
Compact Substation Applications:
- Urban power distribution
- Industrial zones with space constraints
- Solar or wind farm connections
- Temporary or mobile power systems
Conventional Substation Applications:
- Large-scale utility grids
- High-capacity transformer banks
- HV to EHV transmission networks
- Industrial plants with long-term infrastructure

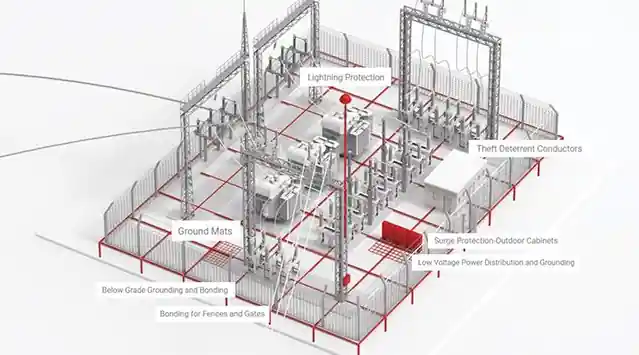
Technical Parameters & Structural Differences
| Parameter | Compact Substation | Conventional Substation |
|---|---|---|
| Installation Time | 1–2 weeks | 2–6 months (depends on scope) |
| Footprint | ~40% smaller | Requires larger site and civil works |
| Components | Integrated into one enclosure | Segmented: switchgear, transformer, etc. |
| Mobility | High (can be relocated) | Stationary, permanent structure |
| Voltage Range | Up to 36 kV (typically) | Can go up to 400 kV or more |
| Cooling Type | Often dry-type or oil-immersed in sealed box | Open-air or oil pit cooling |
| Standard Compliance | IEC 62271-202, ANSI C37 | IEC 61936, IEEE Std 80 |
Market Trend and Industry Adoption
According to IEEMA, MarketsandMarkets, and ABB reports, compact substations are experiencing higher CAGR growth due to:
- Increasing urbanization and land scarcity
- Renewable integration (solar, wind)
- Modular project timelines (e.g., EPC contracts)
- Improved prefabrication and smart monitoring technology
Major players like Schneider Electric, Siemens, and Eaton offer both conventional and compact substation systems to meet regional grid demands.

Selection Criteria: Which One to Choose?
Choose a Compact Substation when:
- Site space is limited or temporary
- Quick installation is needed (urban or industrial)
- Power rating is moderate (≤36kV)
- Indoor or outdoor weatherproof enclosure is required
Choose a Conventional Substation when:
- High-capacity loads or transmission voltage is involved
- Scalability and future expansion are expected
- Maintenance access to each section is critical
Benefits Summary
- Compact Substation Advantages:
- Plug-and-play design
- Faster deployment
- Safer enclosed system
- Better aesthetics in urban areas
- Conventional Substation Advantages:
- Fully customizable
- Easier to maintain at large scale
- Handles high voltage and complex layouts
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Yes. Most compact substations come with IP54 or higher enclosures, suitable for outdoor deployment under IEC 62271-202.
They are typically modular but not scalable in the same way as conventional substations. For long-term growth, conventional designs are better.
They may have a higher initial unit cost, but they save significantly on civil works, installation time, and long-term mobility.
Both compact and conventional substations play vital roles in modern power distribution. Choosing between them depends on voltage requirements, available space, future scalability, and project timeline. As grid modernization and renewable expansion accelerate, compact substations provide an increasingly viable solution for fast, reliable, and space-efficient power distribution.
PINEELE offers certified compact substation guide units and custom solutions for diverse grid environments, from residential zones to utility-scale power networks.
Get a printable version of this page as a PDF.