When it comes to designing safe, efficient, and reliable low voltage electrical panels, one standard stands above the rest: IEC 61439-1.
Published by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), IEC 61439-1 defines the general requirements for low-voltage switchgear and controlgear assemblies. It applies to everything from power distribution boards in buildings to motor control centers in industrial facilities.
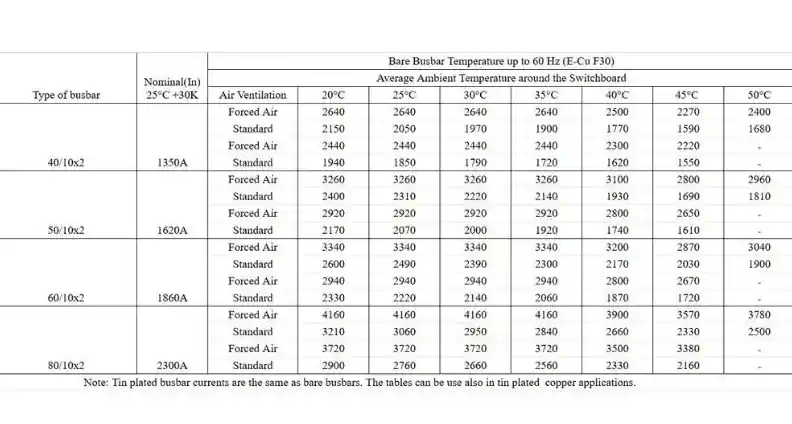
Why IEC 61439-1 Matters
In today’s fast-evolving electrical landscape, the demand for certified, standardized components is higher than ever. IEC 61439-1 was developed to replace the outdated IEC 60439 series, addressing limitations and aligning panel design with real-world applications.
Rather than focusing only on type testing, the new standard introduces a design verification approach, allowing custom-built and modular systems to meet the same safety and performance expectations as factory-tested assemblies.
In practical terms, this means:
- Manufacturers can build safer and more customized panels.
- Contractors can rely on standard performance levels.
- Project owners enjoy easier compliance with international codes.
Who Needs to Follow IEC 61439-1?
This standard is crucial for a wide range of stakeholders, including:
- Panel builders creating low-voltage assemblies
- Electrical engineers designing industrial or commercial systems
- Facility managers ensuring ongoing safety and compliance
- OEMs and contractors bidding on international or government projects
Any switchgear enclosure used for distributing or controlling electricity under 1000 volts AC or 1500 volts DC is expected to conform to IEC 61439-1 — either directly or via complementary parts such as IEC 61439-2 or 61439-3.
Key Principles of IEC 61439-1
- Design Verification, Not Just Type Testing
Instead of requiring all assemblies to be type-tested by a central lab, IEC 61439-1 allows manufacturers to verify their designs using standard-compliant calculations and simulations. This flexibility promotes innovation without sacrificing safety. - Clear Roles and Responsibilities
It distinguishes between:- Original Manufacturer: The entity responsible for the verified design
- Assembly Manufacturer: The one who builds and verifies each physical unit
- Modular Testing Approach
Each functional component of a panel — including insulation, mechanical durability, temperature rise, and fault protection — is verified independently. - Routine Tests for Every Panel
Every unit must undergo visual inspection, wiring checks, and dielectric strength tests before being delivered.
Where Is IEC 61439-1 Applied?
From high-rise buildings to solar farms, IEC 61439-1 plays a role in almost every low-voltage installation:
- Industrial machinery and production lines
- Office buildings and commercial centers
- Apartment complexes and housing blocks
- Electrical substations and grid-connected systems
- Renewable energy systems (solar inverters, battery banks)
- Smart control centers and SCADA-linked switchgear

Comparison: IEC 61439-1 vs IEC 60439
| Feature | IEC 60439 | IEC 61439-1 (Current) |
|---|---|---|
| Testing Method | Type-tested | Design verification |
| Cross-manufacturer builds | Not permitted | Modular components ok |
| Responsibility Definition | Vague | Clearly defined |
| Temperature Rise Handling | Basic | Full load testing |
| Panel Customization | Limited | Fully supported |
Common Specifications in IEC 61439-1 Panels
| Specification | Typical Range |
|---|---|
| Rated operational voltage | Up to 1000V AC / 1500V DC |
| Rated short-time current (Icw) | Up to 100kA for 1s or 3s |
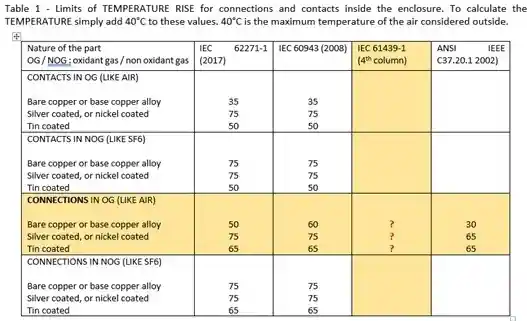
| Temperature rise limit | ≤ 70°C over ambient |
| Degree of protection (IP) | IP30 to IP65 |
| Forms of separation | Form 1 to Form 4b |
These figures may vary depending on application, component design, and enclosure configuration.
The Future of IEC 61439-1
With increasing global demand for standard-compliant electrical panels, IEC 61439-1 is expected to remain the dominant reference for years to come. As smart grids, renewable energy, and modular infrastructure expand, panel builders and manufacturers aligning with IEC 61439-1 will be in a strong competitive position.
Governments, architects, and EPC contractors are now frequently requiring IEC compliance in technical specifications, making it a must-have for anyone supplying switchgear solutions on the global stage.
Conclusion: Why IEC 61439-1 Deserves Your Attention
Whether you’re designing a panel for a high-tech industrial facility or bidding on an infrastructure project in the Middle East, knowing and applying IEC 61439-1 isn’t optional — it’s strategic.
Compliance not only ensures safety and durability, but also unlocks new markets, improves quality assurance, and builds client trust.
If your switchgear isn’t IEC 61439-1 compliant, it’s time to upgrade.
FAQ: IEC 61439-1 Explained
Q1: What is IEC 61439-1?
A: IEC 61439-1 is the international standard that defines the general rules for low voltage switchgear assemblies. It ensures electrical panels meet global safety and performance criteria.
Q2: Who needs to comply with IEC 61439-1?
A: Panel builders, electrical engineers, contractors, and facility managers involved in manufacturing or installing low-voltage switchgear must ensure compliance.
Q3: What is the difference between IEC 61439-1 and IEC 60439?
A: IEC 61439-1 replaces the older IEC 60439 series with clearer responsibilities, modular design verification, and stricter safety protocols.
Q4: Is IEC 61439-1 required for solar or renewable systems?
A: Yes. Many solar farms and green energy projects use IEC 61439-1 certified switchgear for safety, modularity, and global compliance.
Q5: Does IEC 61439-1 apply to residential panels?
A: For residential distribution boards, IEC 61439-3 is more specific, but Part 1 still applies as the base standard for general requirements.