Transformers are fundamental components in modern electrical distribution networks, ensuring the safe and efficient transfer of electrical energy across various voltage levels. Among the different types, oil-filled transformers represent a widely used and time-tested solution. But what specifically makes them a preferred choice? Understanding the distinct advantages of oil-filled transformers is crucial for engineers, utility managers, and industrial operators. This article explores the key benefits, technical attributes, common applications, and compares them against alternatives like dry-type transformers, providing insights backed by industry knowledge from sources like ABB and IEEE.
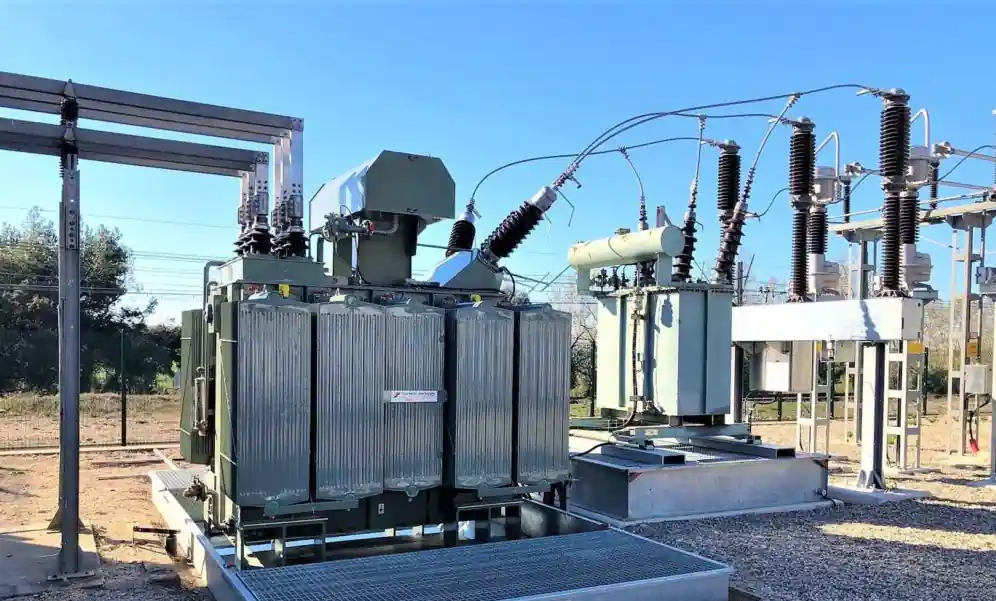

Understanding the Technology: What is an Oil-Filled Transformer?
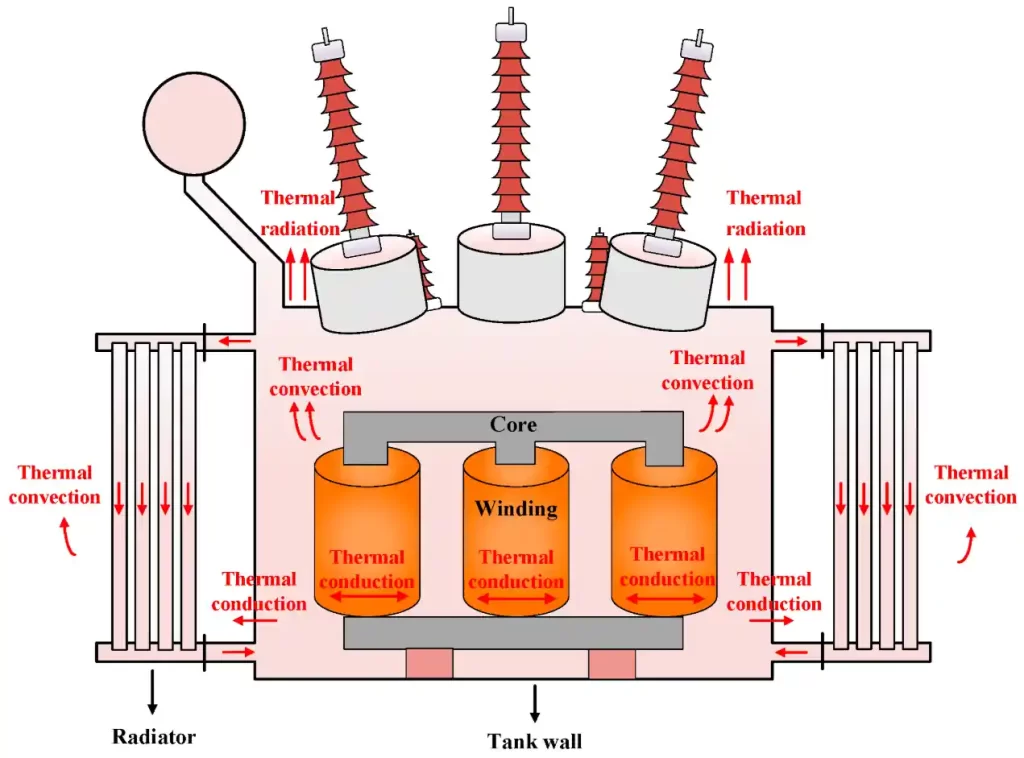
An oil-filled transformer, often referred to as an oil-immersed transformer, utilizes highly refined mineral oil (or sometimes synthetic/natural ester insulating fluids) for two critical functions: cooling and insulation. The transformer’s active core and windings are submerged in this oil within a sealed tank. This design effectively dissipates the heat generated during operation and provides high dielectric strength to prevent electrical arcing between components. This inherent design ensures reliable performance in diverse environments, from indoor vaults to outdoor substations.
Where Are Oil-Filled Transformers Used? Key Application Areas
The unique characteristics and advantages of oil-filled transformers make them ideal for a wide range of demanding applications:
- Power Generation and Transmission: Essential in power plants and high-voltage substations.
- Industrial Facilities: Ideal for factories and plants with high load demand.
- Distribution Networks: Common in both urban and rural substations.
- Renewable Energy Projects: Used in solar farms and wind turbine applications.
- Transportation Infrastructure: Employed in railway systems and traction substations.

Unpacking the Key Advantages of Oil-Filled Transformers
1. Superior Cooling Efficiency
Insulating oil offers excellent thermal conductivity and heat capacity, enabling the transformer to stay cool during high loads. According to ABB, oil-filled units often outperform dry-type transformers when it comes to sustained overloads.
2. High Power and Voltage Capacity
Oil-filled transformers can easily handle ratings above 5000 kVA, reaching into hundreds of MVA, making them ideal for grid guide-scale and industrial use.
3. Long Lifespan
Thanks to efficient cooling and sealed designs, these units can operate for 25–40 years when properly maintained.
4. Cost-Effectiveness
Despite periodic maintenance, oil-filled transformers typically offer lower lifetime costs due to better efficiency and durability.
5. Excellent Overload Tolerance
The oil’s thermal mass enables oil-immersed transformers to handle temporary spikes in demand more effectively than dry types.
Oil-Filled vs. Dry-Type Transformers: A Comparative Summary
| Feature | Oil-Filled Transformers | Dry-Type Transformers | Key Difference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cooling Medium | Mineral/Synthetic Oil | Air/Natural Convection | Liquid vs. Air Cooling |
| Maintenance Needs | Requires oil testing | Minimal | Oil handling vs. dry design |
| Fire Safety | Needs containment/fire systems | Naturally fire-resistant | Higher fire risk for oil types |
| Installation Location | Indoor & Outdoor | Mostly Indoor | Flexibility vs. Safety Requirements |
| Power Capacity | High (up to grid-scale) | Lower (typically under 20 MVA) | Suitable for high-demand use cases |
| Energy Efficiency | Slightly higher on average | Slightly lower | Oil improves heat dissipation |
Standards from IEEE and IEC help guide selection based on use case, power level, and environmental safety.
Market Trends and Global Standards
Oil-filled transformers remain a vital part of the global power infrastructure. Reports from Markets and Markets indicate steady growth in demand due to increasing electrification and infrastructure development. Leading standards include IEC 60076, IEEE C57, and ANSI specifications which help ensure performance, safety, and environmental compliance.
Choosing the Right Transformer
Here are some guidelines to help you select between oil-filled and dry-type transformers:
- Load Demand: Choose oil-filled for high-capacity or fluctuating load environments.
- Environment: For outdoor or extreme temperature locations, oil-filled is preferred.
- Fire Risk: Dry-type may be better in fire-sensitive or enclosed indoor areas.
- Maintenance Capability: Ensure the facility can perform oil testing if choosing oil-filled.
- Budget & ROI: Oil-filled units often offer better return on investment over time.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
A: With modern designs, including sealed tanks, pressure relief valves, and containment bunds, oil-filled transformers are safe for outdoor use when installed per IEEE standards.
A: Annual oil testing for dielectric strength, moisture, and acidity is typical. Preventive maintenance ensures long life and stable performance.
A: Yes. Many are designed to operate between -40°C to +50°C, depending on the cooling type and oil used.
The advantages of oil-filled transformers—from efficient cooling and high voltage handling to long lifespan and better overload tolerance—make them a smart choice for many utility and industrial needs. While dry-type transformers serve well in specific indoor and fire-sensitive environments, oil-filled designs continue to dominate outdoor and high-demand applications globally. Backed by industry standards and a strong performance record, they remain a reliable asset in electrical infrastructure.