In the realm of power distribution, transformers are vital components ensuring voltage regulation guide, grid efficiency, and safe electrical energy transfer. Among the many transformer types, oil-immersed and dry-type transformers are the two most widely used, each offering specific advantages depending on application, environment, and safety requirements.
What Are Oil-Immersed Transformers?
Oil-immersed transformers are filled with insulating oil that provides both cooling and electrical insulation. The oil circulates around the core and windings, dissipating heat and protecting internal components from environmental stress.
Advantages:
- Superior cooling capacity
- High overload tolerance
- Longer life expectancy when maintained properly
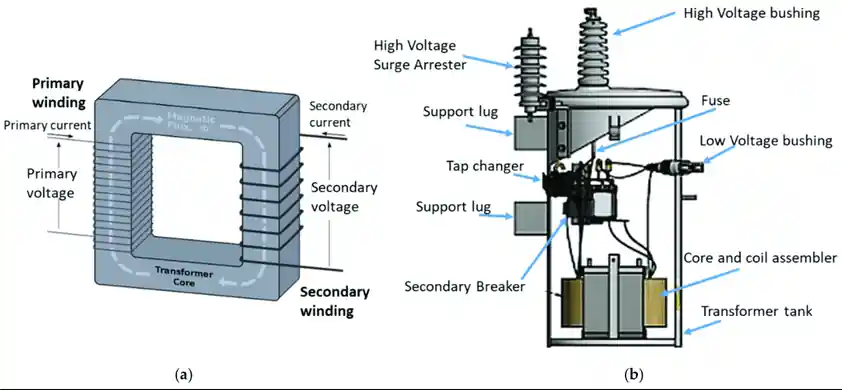
What Are Dry-Type Transformers?
Dry-type transformers, in contrast, use air as the cooling medium and solid insulation materials like resin to encase windings. They are commonly used in indoor, fire-prone, or environmentally sensitive areas where oil leakage presents a hazard.
Advantages:
- No risk of oil leakage or fire
- Low maintenance
- Safe for indoor or enclosed spaces

Application Areas
| Transformer Type | Common Use Cases |
|---|---|
| Oil-Immersed | Outdoor substations, utility grids, rural areas |
| Dry-Type | Hospitals, commercial buildings, data centers |
Market Trends & Industry Adoption
According to a 2024 report by IEEE, the market for dry-type transformers is growing rapidly, especially in urban smart grid deployments and renewable energy systems. However, oil-immersed units remain dominant in high-voltage and utility-scale applications due to their robustness.
ABB and Schneider Electric have both emphasized that energy efficiency and eco-design are key drivers in Transformer guide evolution. Innovations in resin-encased coils and eco-friendly transformer oil are further bridging the gap between the two technologies.
Technical Comparison
| Feature | Oil-Immersed Transformer | Dry-Type Transformer |
|---|---|---|
| Cooling Medium | Mineral or synthetic oil | Air / Epoxy Resin |
| Fire Hazard | Higher due to flammable oil | Lower due to no oil |
| Maintenance | Requires oil testing/filtering | Minimal |
| Installation Environment | Outdoor preferred | Indoor preferred |
| Noise Level | Lower (better damping) | Slightly higher |
| Initial Cost | Lower | Higher |
Key Differences
The main difference lies in the cooling method and safety profile. Oil-filled transformers are more suited for high-capacity outdoor use, while dry-type transformers are ideal for fire-sensitive or space-constrained indoor areas.
In terms of longevity, oil units typically outlast dry types in harsh conditions. However, dry transformers offer greater convenience and flexibility, especially in commercial and institutional setups.
Buying Tips and Selection Guide
When choosing between the two, consider:
- Installation location (indoor/outdoor)
- Fire safety requirements
- Load demands and efficiency goals
- Maintenance capabilities
- Initial and lifecycle cost
If your project involves residential, commercial, or hospital buildings, a dry-type transformer may be the safest, most compact choice. For large-scale utility or industrial use, an oil-immersed unit offers greater reliability.
Authority References
- IEEE Xplore on Transformer Technologies
- ABB: Dry vs Oil Transformers Whitepaper
- Wikipedia – Transformer Types
- Schneider Electric Technical Guide
FAQs
A: Dry-type transformers are considered safer in terms of fire hazard since they do not contain flammable oil, making them ideal for indoor or sensitive environments.
A: Yes. Dry transformers generally require less ongoing maintenance as there’s no oil to test or replace, unlike oil-immersed units.
A: Not always. For high-power transmission or outdoor use in rugged environments, oil-immersed transformers still hold significant advantages in cost and performance.